GROMACS version: 2022.3
GROMACS modification: No
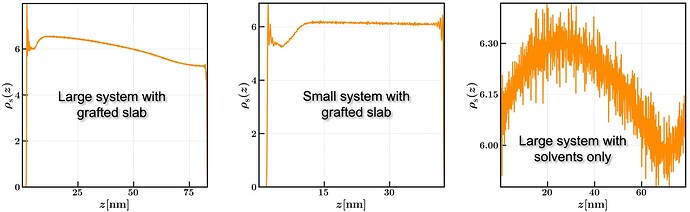
Is there any effect of system size or box size on the solvent density profile? I am running an NPT simulation with semi-isotropic pressure coupling and compressibility applied only along z-axis. The box dimensions are approximately (10,10,80) with 50,000 solvent molecules and PBCs are applied in all directions. For this larger system, I observed an asymmetric, wave-like (sine-wave) density profile along the z-axis. However, using the same MD parameters for a smaller system (box size=(10,10,40) and N_solvents=25,000) yields a symmetric density profile or a flat density profile along the *z-*axis.
Production run .mdp looks like this:
; Production run settings
integrator = md
nsteps = 10000000
dt = 0.002
;Output control(every 50000*0.002 = 100 ps)
nstenergy = 50000
nstxout = 50000
nstlog = 50000
nstvout = 50000
;Bond parameters
continuation = yes ; first dynamics run
constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints
constraints = h-bonds
lincs_iter = 2 ; accuracy of LINCS
lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy
lincs-warnangle = 90 ; warning after rotating the bond
verlet-buffer-tolerance = 0.0001
;Neighbor searching
cutoff-scheme = Verlet
ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cels
nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs
rlist = 1.0
;Electrostatics interaction
rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm)
coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics
pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation
fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT
;Van dar waals interaction
vdw-type = cut-off
rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm)
;Set temperature
tcoupl = v-rescale
tc-grps = system
tau-t = 2
ref-t = 298.15
;Pressure to 1 bar
pcoupl = c-rescale ; Suitable with position restraints
pcoupltype = semiisotropic
ref-p = 1.0 1.0 ; Pressure in xy and z
compressibility = 0 4.5e-5 ; Only compressible in z
tau-p = 4.0
;generate initial velocities
gen-vel = no
;Periodic boundary conditions
pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC
;Dispersion correction
DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme
;COM motion removal
nstcomm = 100
comm-mode = Linear
comm-grps = system
refcoord-scaling = com